Look across just a few brain areas discerns Alzheimer’s vulnerability and resilience components
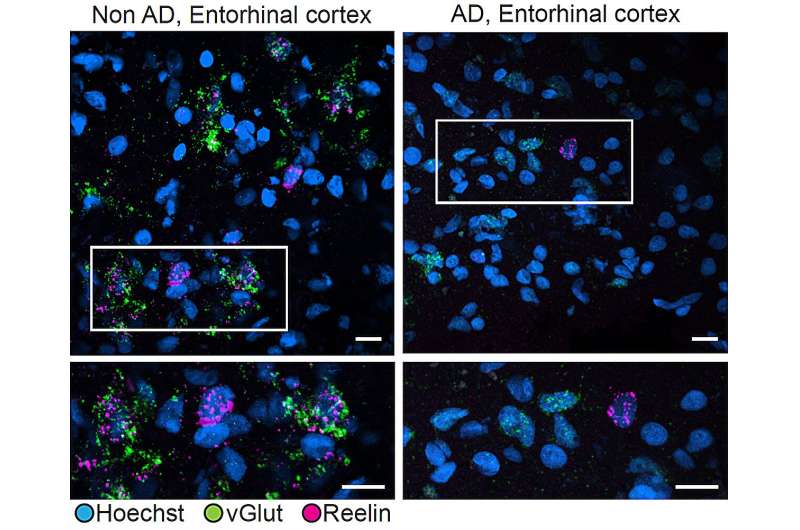
Researchers when compared Reelin expression in excitatory neurons in the entorhinal cortex of people with (appropriate) or without (left) Alzheimer’s illness. In people without the illness, vGlut (green), a marker of excitatory neurons, and Reelin (magenta) were in overall expressed collectively. In people with Alzheimer’s, excitatory cells exhibited noteworthy much less Reelin expression. Credit rating: Tsai Lab/ MIT Picower Institute
An MIT thought revealed in Nature gives recent proof for how notify cells and circuits change into inclined in Alzheimer’s illness, and hones in on various components that would unbiased merit some people prove resilience to cognitive decline, even amid obvious signs of illness pathology.
To spotlight attainable targets for interventions to protect cognition and reminiscence, the authors engaged in a new comparison of gene expression across just a few brain areas in people with or without Alzheimer’s illness, and performed lab experiments to examine and validate their indispensable findings.
Brain cells all have the the same DNA but what makes them vary, each and every of their identification and their process, are their patterns of how they notify these genes. The recent prognosis measured gene expression differences in better than 1.3 million cells of better than 70 cell kinds in six brain areas from forty eight tissue donors, 26 of whom died with an Alzheimer’s prognosis and 22 of whom without.
As such, the thought gives a uniquely huge, some distance-ranging and but detailed accounting of how brain cell process differs amid Alzheimer’s illness by cell form, by brain save, by illness pathology, and by every body’s cognitive evaluation whereas quiet alive.
“Explicit brain areas are inclined in Alzheimer’s and there is a wanted must realize how these areas or explicit cell kinds are inclined,” acknowledged co-senior creator Li-Huei Tsai, Picower Professor of Neuroscience and director of The Picower Institute for Discovering out and Memory and the Rising older Brain Initiative at MIT.
“And the brain is rarely any longer authorized neurons. Or no longer it is many different cell kinds. How these cell kinds might well well unbiased acknowledge otherwise, looking on the save they’re, is something intelligent we are most productive at the delivery of .”
Co-senior creator Manolis Kellis, professor of pc science and head of MIT’s Computational Biology Neighborhood, likened the plan venerable to measure gene expression comparisons, single cell RNA profiling, to being a noteworthy extra developed “microscope” than the ones that first allowed Alois Alzheimer to represent the illness’s pathology better than a century prior to now.
“The save Alzheimer noticed amyloid protein plaques and phosphorylated tau tangles in his microscope, our single-cell ‘microscope’ tells us, cell by cell and gene by gene, about thousands of refined but most famous biological adjustments per pathology,” acknowledged Kellis.
“Connecting this data with the cognitive affirm of patients unearths how cell responses affirm with cognitive loss or resilience, and might merit propose recent ways to treat cognitive loss. Pathology can precede cognitive symptoms by a decade or two ahead of cognitive decline becomes identified. If there’s now not any longer noteworthy we can comprise relating to the pathology at that stage, we can no longer no longer as much as strive to safeguard the cell pathways that protect cognitive feature.”
Hansruedi Mathys, a extinct MIT postdoc in the Tsai Lab, who is now an assistant professor at the College of Pittsburgh, Carles Boix, a extinct graduate student in Kellis’s lab who is now a postdoc at Harvard Scientific College, and Leyla Akay, a graduate student in Tsai’s lab, led the thought examining the prefrontal cortex, entorhinal cortex, hippocampus, anterior thalamus, angular gyrus, and the midtemporal cortex.
The brain samples came from the Non secular Uncover Look and the Skedaddle Memory and Rising older Venture at Skedaddle College.
Neural vulnerability and Reelin
Some of the earliest signs of amyloid pathology and neuron loss in Alzheimer’s occur in reminiscence-targeted areas known as the hippocampus and the entorhinal cortex. In these areas, and in various parts of the cerebral cortex, the researchers were ready to pinpoint a attainable causes why.
One model of excitatory neuron in the hippocampus and 4 in the entorhinal cortex were vastly much less noteworthy in people with Alzheimer’s than in people without.
People with depletion of these cells performed vastly worse on cognitive assessments. Moreover, many inclined neurons were interconnected in a overall neuronal circuit. And authorized as importantly, just a few both without lengthen expressed a protein known as Reelin, or were without lengthen struggling from Reelin signaling.
In all, which potential of this reality, the findings distinctly spotlight especially inclined neurons, whose loss is said to diminished cognition, that portion a neuronal circuit and a molecular pathway.
Tsai nicely-known that Reelin has change into excellent in Alzheimer’s study on legend of of a recent thought of a man in Colombia. He had a uncommon mutation in the Reelin gene that introduced about the protein to be extra packed with life, and was ready to prevent cognitively wholesome at an developed age despite having a solid household predisposition to early-onset Alzheimer’s.
The recent thought presentations that lack of Reelin-producing neurons is said to cognitive decline. Taken collectively, it might possibly well well unbiased imply that the brain benefits from Reelin, but that neurons that comprise it might well most likely be misplaced in no longer no longer as much as some Alzheimer’s patients.
“We can mediate of Reelin as having maybe some roughly maintaining or valuable comprise,” Akay acknowledged. “However we don’t but know what it does or the blueprint it might well most likely confer resilience.”
In further prognosis, the researchers additionally chanced on that particularly inclined inhibitory neuron subtypes known in a old thought from this neighborhood in the prefrontal cortex were additionally fascinated about reelin signaling, further reinforcing the significance of the molecule and its signaling pathway.
To further verify their outcomes, the group without lengthen examined the human brain tissue samples and the brains of two forms of Alzheimer’s model mice. Certain enough, these experiments additionally confirmed a reduction in Reelin-sure neurons in the human and mouse entorhinal cortex.
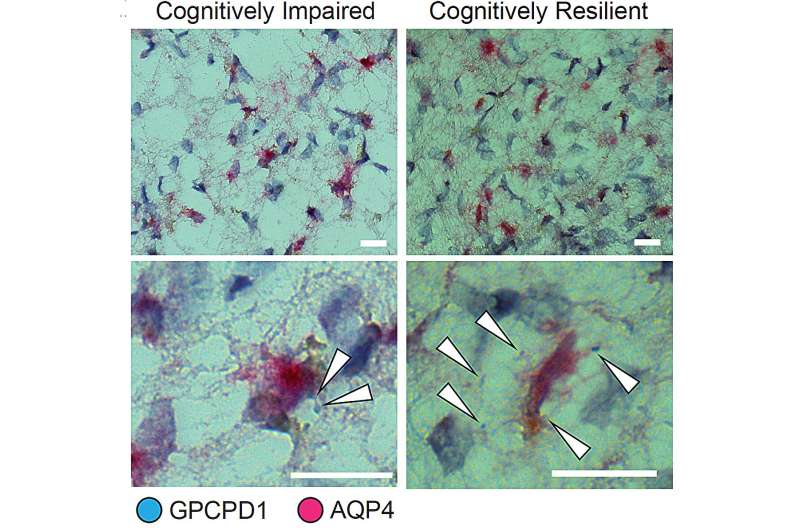
Expression of the gene GPCPD1 in astrocyte cells is said to cognitive resilience in people with Alzheimer’s pathology. Right here white arrows indicate cases of GPCPD1 expression (blue) in astrocyte cells (denoted by AQP4 staining in magenta). There might be noteworthy extra expression in tissue from the cognitively resilient person (appropriate). Credit rating: Tsai Lab/MIT PIcower Institute
Resilience connected to choline metabolism in astrocytes
To search out components that might protect cognition, even amid pathology, the group examined which genes, in which cells, and in which areas, were most closely connected to cognitive resilience, which they outlined as residual cognitive feature, above the conventional cognitive loss anticipated given the noticed pathology.
Their prognosis yielded a unpleasant and notify resolution: across just a few brain areas, astrocytes that expressed genes connected to antioxidant process and with choline metabolism and polyamine biosynthesis were vastly connected to sustained cognition, even amid excessive stages of tau and amyloid.
The outcomes bolstered old study findings led by Tsai and Susan Lundqvist in which they confirmed that dietary supplement of choline helped astrocytes address the dysregulation of lipids attributable to the most well-known Alzheimer’s possibility gene, the APOE4 variant.
The antioxidant findings additionally pointed to a molecule that shall be chanced on as a dietary supplement, spermidine, that would unbiased have anti-inflammatory properties, though such an association would want further work to be established causally.
As ahead of, the group went beyond the predictions from the single-cell RNA expression prognosis to attain instruct observations in the brain tissue of samples. Americans who came from cognitively resilient people indeed confirmed increased expression of just among the astrocyte-expressed genes predicted to be connected to cognitive resilience.
Glossy prognosis plan, delivery dataset
To analyze the mountains of single-cell data, the researchers developed a recent sturdy methodology per groups of coordinately-expressed genes (identified as “gene modules”), thus exploiting the expression correlation patterns between functionally-connected genes in the the same module.
“In arrangement, the 1.3 million cells we surveyed might utilize their 20,000 genes in an colossal quantity of various combinations,” explains Kellis. “In discover, on the opposite hand, we quiz a noteworthy smaller subset of coordinated adjustments. Recognizing these coordinated patterns permits us to infer noteworthy extra sturdy adjustments, on legend of they’re per just a few genes in the the same functionally-connected module.”
He supplied this analogy: With many joints of their our bodies, people might pass in all forms of loopy ways, but in discover they engage in many fewer coordinated actions, love walking, working, or dancing. The recent plan permits scientists to title such coordinated gene expression applications as a neighborhood.
While Kellis and Tsai’s labs already reported just a few noteworthy findings from the dataset, the researchers save a matter to that many extra most likely well-known discoveries quiet wait to be chanced on in the trove of knowledge. To facilitate such discovery, the group posted at hand analytical and visualization instruments along side the info on Kellis’s online page.
“The dataset is so immensely rich. We targeted on most productive a few facets which shall be salient that we dangle are very, very attractive, but by no blueprint have we exhausted what shall be learned with this dataset,” Kellis acknowledged. “We save a matter to many extra discoveries ahead, and we hope that young researchers (of all ages) will dive appropriate in and surprise us with many extra insights.”
Going ahead, Kellis acknowledged, the researchers are studying the adjust circuitry connected to the differentially expressed genes, to realize the genetic variants, the regulators, and various driver components that shall be modulated to reverse illness circuitry across brain areas, cell kinds, and various stages of the illness.
More data:
Manolis Kellis, Single-cell multiregion dissection of Alzheimer’s illness, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07606-7. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07606-7
This story is republished courtesy of MIT Files (internet.mit.edu/newsoffice/), a most neatly-liked save that covers news about MIT study, innovation and educating.
Citation:
Look across just a few brain areas discerns Alzheimer’s vulnerability and resilience components (2024, July 24)
retrieved 26 July 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-07-just a few-brain-areas-discerns-alzheimer.html
This story is discipline to copyright. Besides any shapely dealing for the cause of non-public thought or study, no
segment will be reproduced without the written permission. The swear is supplied for data capabilities most productive.