Safety Flaws in Well-liked ML Toolkits Allow Server Hijacks, Privilege Escalation
[ad_1]
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered almost two dozen safety flaws spanning 15 completely different machine studying (ML) associated open-source initiatives.
These comprise vulnerabilities found each on the server- and client-side, software program provide chain safety agency JFrog mentioned in an evaluation printed final week.
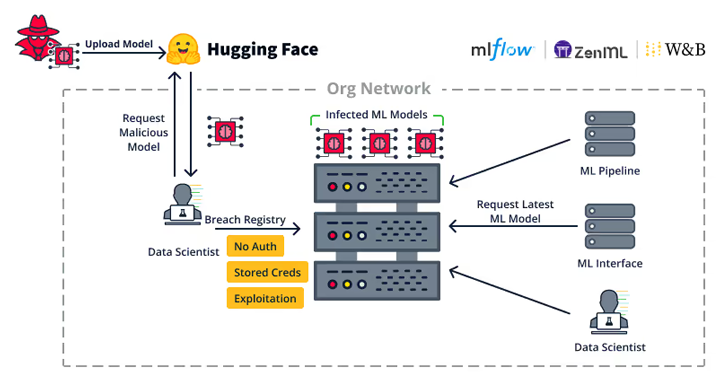
The server-side weaknesses “permit attackers to hijack vital servers within the group equivalent to ML mannequin registries, ML databases and ML pipelines,” it said.
The vulnerabilities, found in Weave, ZenML, Deep Lake, Vanna.AI, and Mage AI, have been damaged down into broader sub-categories that permit for remotely hijacking mannequin registries, ML database frameworks, and taking on ML Pipelines.
A quick description of the recognized flaws is beneath –
- CVE-2024-7340 (CVSS rating: 8.8) – A listing traversal vulnerability within the Weave ML toolkit that enables for studying recordsdata throughout the entire filesystem, successfully permitting a low-privileged authenticated person to escalate their privileges to an admin function by studying a file named “api_keys.ibd” (addressed in version 0.50.8)
- An improper entry management vulnerability within the ZenML MLOps framework that enables a person with entry to a managed ZenML server to raise their privileges from a viewer to full admin privileges, granting the attacker the flexibility to switch or learn the Secret Retailer (No CVE identifier)
- CVE-2024-6507 (CVSS rating: 8.1) – A command injection vulnerability within the Deep Lake AI-oriented database that enables attackers to inject system instructions when importing a distant Kaggle dataset as a result of an absence of correct enter sanitization (addressed in version 3.9.11)
- CVE-2024-5565 (CVSS rating: 8.1) – A immediate injection vulnerability within the Vanna.AI library that might be exploited to realize distant code execution on the underlying host
- CVE-2024-45187 (CVSS rating: 7.1) – An incorrect privilege task vulnerability that enables visitor customers within the Mage AI framework to remotely execute arbitrary code by means of the Mage AI terminal server as a result of the truth that they’ve been assigned excessive privileges and stay energetic for a default interval of 30 days regardless of deletion
- CVE-2024-45188, CVE-2024-45189, and CVE-2024-45190 (CVSS scores: 6.5) – A number of path traversal vulnerabilities in Mage AI that permit distant customers with the “Viewer” function to learn arbitrary textual content recordsdata from the Mage server by way of “File Content material,” “Git Content material,” and “Pipeline Interplay” requests, respectively
“Since MLOps pipelines might have entry to the group’s ML Datasets, ML Mannequin Coaching and ML Mannequin Publishing, exploiting an ML pipeline can result in a particularly extreme breach,” JFrog mentioned.
“Every of the assaults talked about on this weblog (ML Mannequin backdooring, ML information poisoning, and many others.) could also be carried out by the attacker, relying on the MLOps pipeline’s entry to those assets.
The disclosure comes over two months after the corporate uncovered greater than 20 vulnerabilities that might be exploited to focus on MLOps platforms.
It additionally follows the discharge of a defensive framework codenamed Mantis that leverages immediate injection as a solution to counter cyber assaults Massive language fashions (LLMs) with greater than over 95% effectiveness.
“Upon detecting an automatic cyber assault, Mantis vegetation fastidiously crafted inputs into system responses, main the attacker’s LLM to disrupt their very own operations (passive protection) and even compromise the attacker’s machine (energetic protection),” a gaggle of teachers from the George Mason College said.
“By deploying purposefully weak decoy providers to draw the attacker and utilizing dynamic immediate injections for the attacker’s LLM, Mantis can autonomously hack again the attacker.”
[ad_2]
Source link